Cancer in China
Source:Science Direct
From:Taipei World Trade Center Liaison Office in Chennai
Update Time:2018/12/17
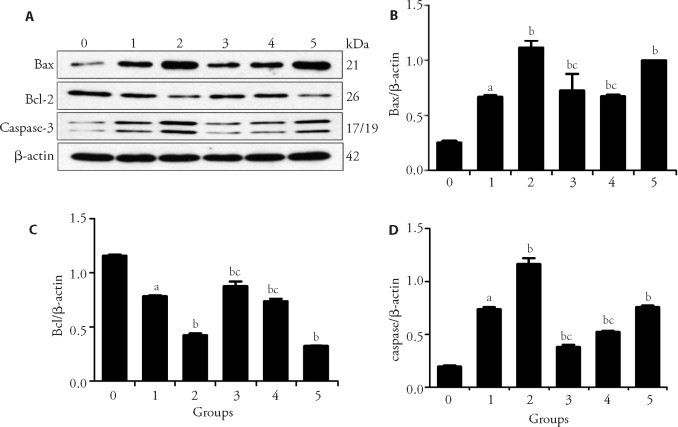
Effects of E on Bcl-2, Bax, and caspase-3 protein expression in A549 cells under chemical-induced hypoxia
INTRODUCTION
‘Lung cancer has the highest death rate among all types of cancers. In 2017 the most common cause of cancer death was still lung cancer in the United States, which contributes to more than a quarter of cancer mortality among all tumor types. In China, lung cancer is also the leading cause of cancer death for both males and females. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 80%-85% of all lung cancers. Cisplatin-based chemotherapy has been widely used for patients with NSCLC in recent years. Although chemotherapy and targeted therapy have been improved in recent decades, the efficacy of chemotherapy for NSCLC is modest at present, and the 5-year survival rate of NSCLC is still unsatisfactory.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has been used in treatment of lung cancer for many years in China. The method of promoting Qi and activating blood is commonly used in the treatment. The combination of Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongolici) and Ezhu (Rhizoma Curcumae Phaeocaulis) is one of the most common combinations in the method. The effective active ingredients of Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongolici) and Ezhu (Rhizoma Curcumae Phaeocaulis), such as Astragalus saponins, Astragalus polysaccharide, β-elemene and Curcumin, have been reported to have anti-cancer effects. The research into the compatibility of Chinese herbs has risen from the herbal pieces level to the component formula level and the uniform experimental design has become a new valuable method in the compatibility research of Chinese medicine drugs.
In this study, we used the uniform design method with a 4-factor and 8-level table to determine the optimal combination (E) of four components in Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongolici) and Ezhu (Rhizoma Curcumae Phaeocaulis), namely Astragalus polysaccharide, Astragalus saponins, Curcumin and β-Elemene. Changes in the inhibition of A549 cell proliferation were observed as screening indices, and regression analysis was used to determine E. Using the chemical approach (CoCl2) to simulate hypoxia, we analyzed the expression of Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3 in A549 lung cancer cells treated with various doses of E.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Drugs and reagents
Astragalus saponins and polysaccharide were purchased from Efebio Co., Ltd., (Shanghai, China). β-Elemene and Curcumin were purchased from the National Institutes for Food and Drug Control (Beijing, China). Antibody against Bax and antibody against β-actin were obtained from Abcam (Cambridge, UK). Antibody against caspase-3 was obtained from Cell Signaling Technology Inc. (Danvers, MA, USA). Antibody against Bcl-2, goat anti-rabbit IgG-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and goat anti-mouse IgG-HRP were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc. (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Trizol reagent was obtained from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). Other reagents included a HiFiMMLVcDNA First Strand Synthesis kit, Ultra-pure RNA extraction kit. An Annexin V-FITC/PI Apoptosis Detection kit and UltraSYBR mixture were obtained from CWbio Co., Ltd., (Beijing, China). A Cell Titer 96® AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay (MTS) was purchased from Promega (Madison, WI, USA). Cisplatin injection was obtained from Hospira (Mulgrave, Australia). CoCl2 was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA).
Cell culture and treatments
The A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cell line was purchased from the Cell Center of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (Beijing, China). The cells were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 medium (RPMI-1640) (Gibco, NY, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Sijiqing, Hangzhou, China) and an antibioticmixture of Penicillin-Streptomycin Solution (Pasching, Austria). The cells were seeded on culture plates for each experiment and grown at 37 °C with 5% CO2. Astragalus saponins, Astragalus polysaccharide, Curcumin and β-Elemene were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and diluted with RPMI-1640. The final concentration of DMSO never exceeded 5‰ (v/v). CoCl2 was dissolved in sterile water for injection and diluted with RPMI-1640. Cisplatin was diluted with RPMI-1640.
In this study, the uniform design method was used to optimize the most effective component formula of Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongolici) and Ezhu (Rhizoma Curcumae Phaeocaulis) in on effect of the proliferation of A549 lung cancer cells. A uniform design method with a 4-factor and 8-level table U8 (84) was used to optimize the proportions of four component in Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongolici) and Ezhu (Rhizoma Curcumae Phaeocaulis), namely, Astragalus polysaccharide (X1), Astragalus saponins (X2), Curcumin (X3), and β-elemene (X4).Moreover, changes in the cellular proliferation inhibition rate (CPIR) were observed as evaluation indicator, and regression analysis was used to determine E.
RESULTS
Proliferation inhibition of A549 cells
A uniform design method with a 4-factor and 8-level table was used to optimize the proportions of four components in Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongolici) and Ezhu (Rhizoma Curcumae Phaeocaulis) (Table 1). All CPIR observations of the eight uniform design groups were analyzed by stepwise regression analysis using SPSS 17.0 statistical software. Screening α into = α out = 0.15, two factors entered the model (X1 and X3), R2 = 0.805, it indicated that two influencing factors resulted in 80.5% CPIR variation and the model was relatively satisfactory. The optimal regression equation is = 0.003X1 + 0.26X3-0.503. Based on the partial regression coefficient, higher levels of X1 and X3 led to a higher CPIR. X2 and X4 were removed during the regression process, it indicated that changes of X2 and X4 did not affect the changes of CPIR. Therefore, the optimal test scheme obtained by the uniform design (E) was 200 mg/L Astragalus polysaccharide (X1) and 32 mg/L curcumin (X3).
Apoptotic induction of A549 cells under chemical-induced hypoxia
Apoptosis was analyses by flow cytometry in A549 cells. Results showed no significant difference between group 0 and group CoCl2 (P > 0.05). Compared with group 0, group DDP + CoCl2, 1E + CoCl2 and 2E + CoCl2 promoted the apoptosis rates of A549 cells (P < 0.05), and the apoptosis rates of group 0.5E + CoCl2, 1E + CoCl2 and 2E + CoCl2 were dose dependent. The apoptosis rates of the group 1E + CoCl2 and the group 2E + CoCl2 had no statistically significant difference compared with the group DDP + CoCl2 (P > 0.05).’
Source and URL : Science Direct 。https://www.sciencedirect.com